The promotion of neurogenesis is usually a promising technique to enhance and restore neuronal operate in neurodegenerative illnesses. Nerve progress issue (NGF) performs a key function in neurite outgrowth and synaptic formation throughout mind restore stage. Nowadays, there are a number of research on the growing strategies to reinforce the endogenous NGF exercise for therapy and restore the neuronal operate.
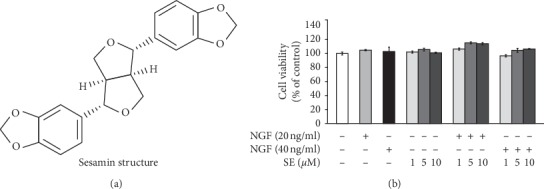
In this research, the potentiating impact of sesamin, a serious lignan in sesame seeds (Sesamum indicum) and oil, on NGF-induced neurogenesis and its concerned mechanisms have been firstly reported. Sesamin successfully enhanced the PC12 neuron-like cell differentiation and neurite size under inadequate situations of NGF.
The neuronal markers together with synaptophysin and growth-associated protein-43 together with the synaptic connections have been considerably elevated in mixture therapy between sesamin and NGF.
Moreover, sesamin additionally elevated the extent of phospho-ERK1/2 and SIRT1 protein, an necessary regulatory protein of the neurogenesis course of. The neurogenesis was blocked by the particular SIRT1 inhibitor, JGB1741, suggesting that the neuritogenic impact of sesamin was related to SIRT1 protein modulation.
Taken collectively, the potentiating impact of sesamin on NGF-induced neurogenesis in this discovering might be used for different therapy in neurodegenerative illnesses, together with Alzheimer’s illness.
Retrograde nerve progress issue signaling abnormalities in familial dysautonomia.
Familial dysautonomia (FD) is probably the most prevalent type of hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy (HSAN). In FD, a germline mutation in the Elp1 gene results in Elp1 protein lower that causes sympathetic neuron demise and sympathetic nervous system dysfunction (dysautonomia).
Elp1 is finest generally known as a scaffolding protein inside the nuclear hetero-hexameric transcriptional Elongator protein advanced, however the way it capabilities in sympathetic neuron survival could be very poorly understood. Here, we recognized a cytoplasmic operate for Elp1 in sympathetic neurons that was important for retrograde nerve progress issue (NGF) signaling and neuron goal tissue innervation and survival.
Elp1 was discovered to bind to internalized TrkA receptors in an NGF-dependent method, the place it was important for sustaining TrkA receptor phosphorylation (activation) by regulating PTPN6 (Shp1) phosphatase exercise inside the signaling advanced. In the absence of Elp1, Shp1 was hyperactivated, resulting in untimely TrkA receptor dephosphorylation, which resulted in retrograde signaling failure and neuron demise.
Inhibiting Shp1 phosphatase exercise in the absence of Elp1 rescued NGF-dependent retrograde signaling, and in an animal mannequin of FD it rescued irregular sympathetic goal tissue innervation. These outcomes counsel that regulation of retrograde NGF signaling in sympathetic neurons by Elp1 could clarify sympathetic neuron loss and physiologic dysautonomia in sufferers with FD.